Automatic Data-Driven Modeling and Norm-Based Dimension Reduction of Process-Oriented and Cooperative Systems for SHM Condition Analysis with Methods of System Identification and Machine Learning on Exposed Struct
The digital transformation is bringing about profound changes in almost all areas of society and technology. In the construction industry in particular, advancing digitalization is opening up new opportunities to plan, monitor, and manage buildings more efficiently throughout their entire life cycle. In this context, the integration of Building Information Modelling (BIM), which enables consistent, model-based planning, execution, and management of facilities, buildings, and infrastructure, with Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) is of central importance. The combination of both approaches paves the way for a digital twin that acts as a virtual representation of a real building. This digital twin allows for the continuous linking of measurement data, status information, and simulation models, thus forming the basis for efficient and transparent data organization throughout the entire life cycle of a structure.
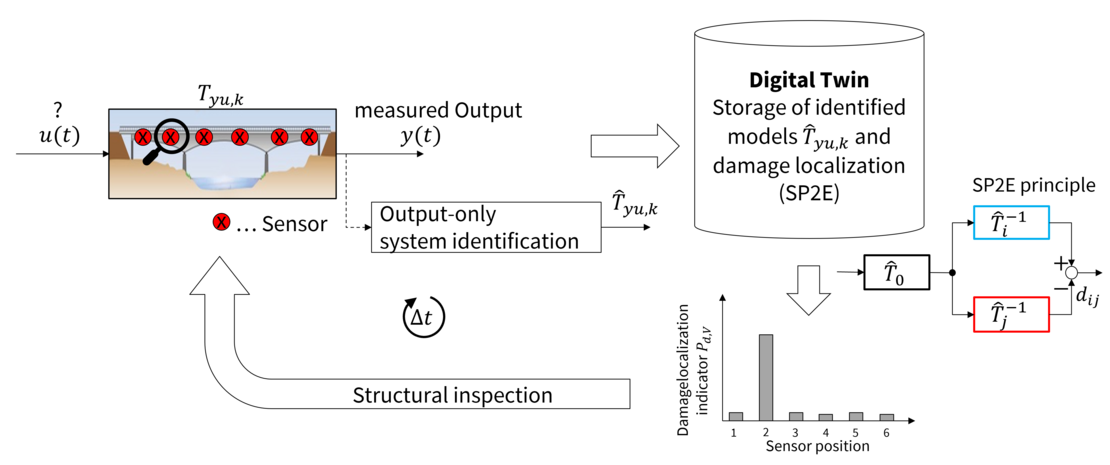
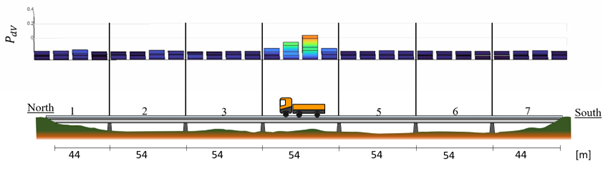
In the first phase of the project, the damage localization method State Projection Estimation Error (SP2E) was further developed, automated, and successfully applied to both laboratory structures and exposed structures, including the I4S technicum and the Flossgraben bridge near Zeitz. The method is based on identified, /-optimized sate space models and enables the detection and spatial allocation of structural changes based on performance differences between reference and operating states.
The second phase of the project focuses on the development of condition indicators and prediction models that enable a longer-term assessment of structural behavior. The aim of the further funding period is to derive physically sound recommendations for action from the prediction and process models obtained via SP2E. These should be applicable in the macro time range of a structure’s service life and thus form a basis for condition-based maintenance, early damage detection, and sustainable infrastructure management.
Team
Publications
Rohrer, M., Moeller, M., & Lenzen, A. “A Testing Field for Studies of Environmental and Operational Effects in Structural Damage Localization of Mechanical Structures” Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2024(1), 3970794.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/3970794Becks et. al. (2024). Neuartige Konzepte für die Zustandsüberwachung und -analyse von Brückenbauwerken – Einblicke in das Forschungsvorhaben SPP100+. Bauingenieur, BD. 99 (2024) Nr. 10.
DOI: doi.org10.37544/0005-6650-2024-10-63Moeller, Max, and Armin Lenzen. "Autonomous Energy-Based Model Order Selection in Parameter State Space Identification Via Cross Gramian and Symmetrizer."; Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 228(2025): 112452; DOI: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2025.112452
Rohrer, Maximilian, et al. "Experimental studies on multi‐scale data‐driven methods within the framework of structural health monitoring" Civil Engineering Design 2025; DOI: 10.1002/cend.202400036
Lenzen, Armin, et al. "A large-scale experiment on the seven span Flossgraben Bridge in operation to investigate damage localization utilizing state projection estimation error (SP2E)" Engineering Structures, 2025, DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2025.121626
List of all publications (including contributions for conferences): https://i4s.htwk-leipzig.de/en/research/publications-1




